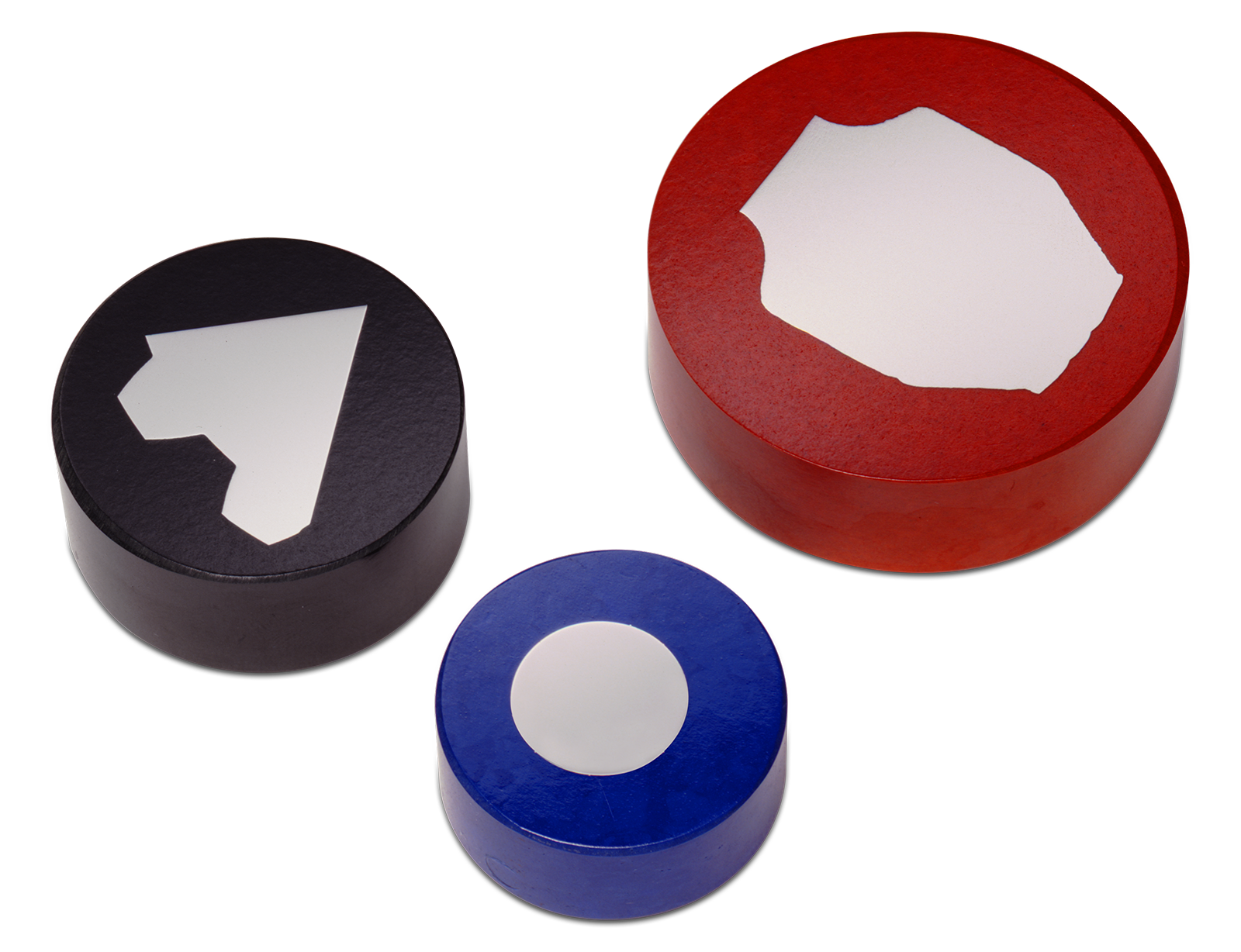
If all you need for your mount is a uniform shape to hold your sample, Bakelite or epoxy would work just fine. It's simply a matter of finding the mounting material that works best with the sample material. But if you need a mounting material that lets you see the sample mounted within, there is no better choice than Lucite.
Read More…LECO Australia mounting posts (Page 1 of 5)
Topics: Mounting, Metallographic Science, MX Series
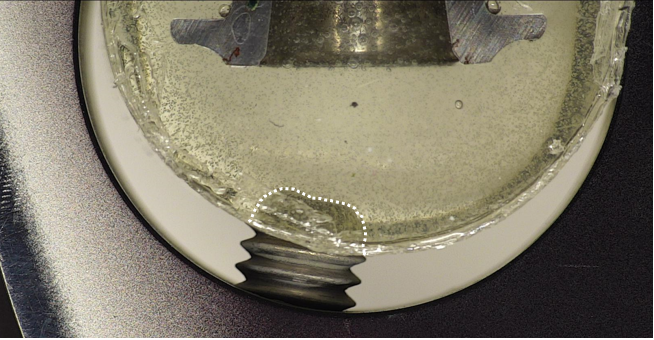
Have you ever let long-cure epoxy mounts cure overnight, only for the setscrew to push into the mount when you went to load it into your grinder/polisher’s fixed specimen holder? When the epoxy is soft, the specimen isn’t secure in the mount or in the specimen holder, and proper grinding and polishing becomes impossible. The eight hour cure time for long cure epoxy means you can’t just whip up a new one; if something goes wrong, you’ve effectively lost an entire day as the replacement also needs eight hours to cure.
But if you left your mounts to cure overnight, shouldn’t that have been more than enough time? What could have gone wrong?
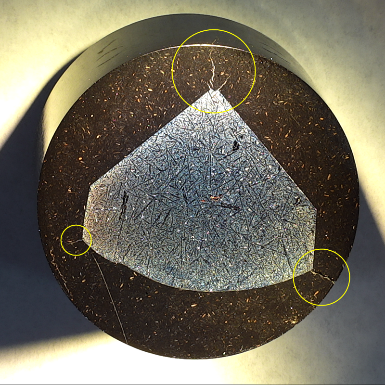
Read More…Cracks in your mount are never a welcome sight. While a scratched specimen doesn’t always have a cracked mount, a mount with radial cracks is far more likely to cause a future scratched specimen. While we covered the scratches in an earlier tip, we can’t ignore the cracks.
There is a certain sort of frustration that comes with putting a completed multi-step metallographic preparation beneath the microscope, taking a look, and seeing a discolored or stained surface. While a few types of stains can be ignored, many stains mean something went wrong during the preparation.
Read More…Bakelite, Lucite, epoxy, or acrylic? Hot or cold? Compression or castable? With all of the options available for mounting materials, it can be difficult to know which one is the best option for your sample or why it even matters. However, your choice of mounting material is important, and it can affect the final quality of your prepared sample.
Read More…Topics: Mounting, Metallographic Science, MX Series